Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Hey there! Today, we're diving into the exciting world of virtualization. If you're curious about what virtualization is all about, virtual machines (VMs), and the mysterious-sounding hypervisor, you're in the right place. So, buckle up and let's embark on this virtual journey together!
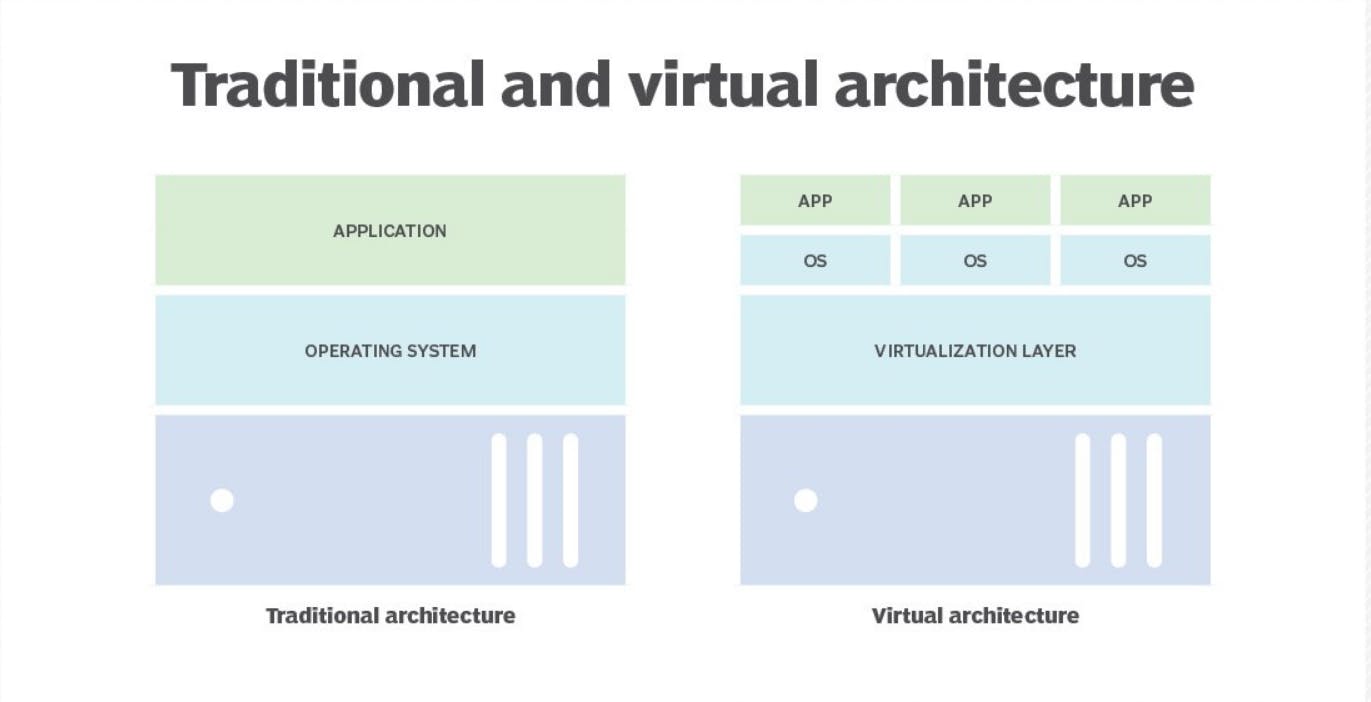
Virtualization, in simple terms, is the process of creating a virtual version of something[O.S], usually a computer system or network resources. It allows you to run multiple operating systems and applications on a single physical machine simultaneously. Pretty cool, right? Let's break it down further.
Virtual Machines (VMs) are at the heart of virtualization. Think of them as independent, self-contained computers that operate within a physical computer. Each VM has its own operating system, applications, and resources, just like a regular physical machine. By running multiple VMs on one physical machine, you can maximize the utilization of resources and achieve better efficiency.
But how does all of this magic happen? That's where the hypervisor comes into play. The hypervisor is a software layer that creates and manages VMs. It acts as the middleman between the physical hardware and the virtual machines, allowing them to share the resources of the host machine while keeping them isolated from each other.
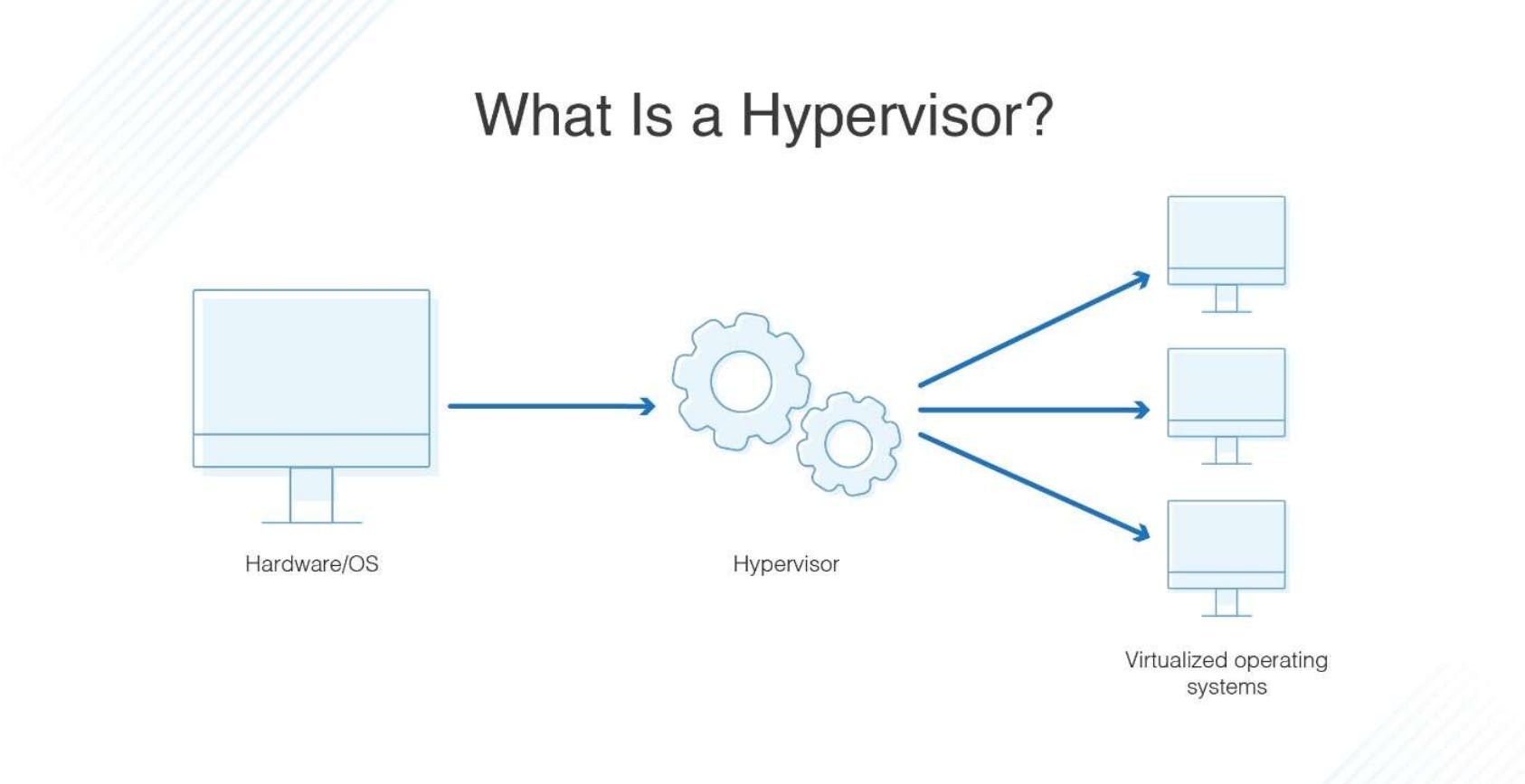
Now, let's talk about the different types of hypervisors. There are two main categories: Type 1 and Type 2.
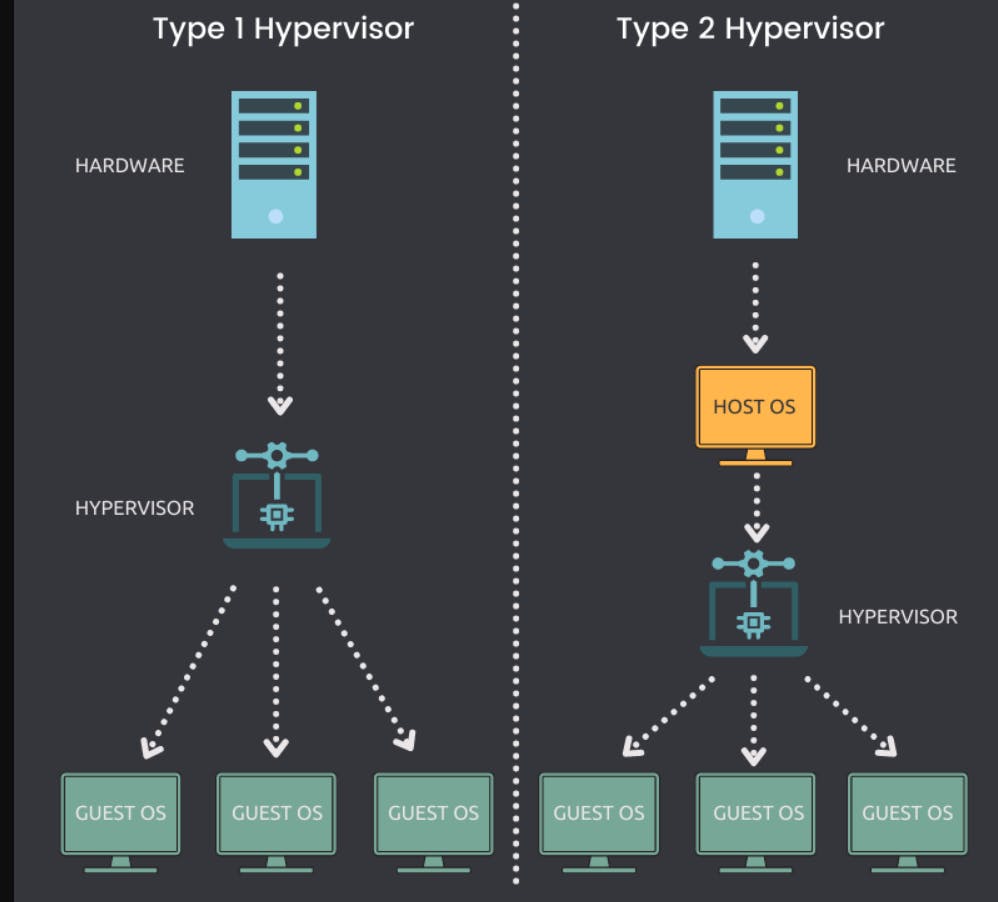
Type 1 hypervisors, also known as bare-metal hypervisors, are installed directly on the physical hardware. They provide a layer of abstraction between the hardware and the VMs. Examples of Type 1 hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Citrix XenServer. These hypervisors are typically used in enterprise environments and data centers where performance and reliability are important.
On the other hand, Type 2 hypervisors run as software on top of an existing operating system. They are commonly used by individuals and small businesses for testing, development, and running multiple operating systems on a personal computer. Popular Type 2 hypervisors include VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, and Microsoft Virtual PC.
Now that you have a basic understanding of virtualization, VMs, and hypervisors, let's talk about the benefits. Virtualization offers several advantages, such as:
Increased Efficiency: By running multiple VMs on a single physical machine, you can make the most out of your hardware resources, reducing costs and energy consumption.
Improved Flexibility: Virtualization allows for easy and quick deployment of new VMs, enabling businesses to scale up or down their infrastructure based on their needs.
Enhanced Security: VMs are isolated from each other, reducing the risk of one VM affecting others. It also enables easier backup and disaster recovery solutions.
Simplified Management: With virtualization, you can centrally manage multiple VMs, making it easier to configure, monitor, and maintain your infrastructure.
Virtualization has revolutionized the IT landscape, enabling businesses and individuals to do more with less. Whether it's consolidating servers, testing new software configurations, or creating development environments, virtualization offers a flexible and efficient solution.
So, there you have it—i hope this introduction to virtualization, virtual machines, and hypervisors has shed some light on this fascinating yet important topic.
Love my content Let's Connet Here: https://www.linkedin.com/in/theshubhamgour/
